Industrial edge computing device assembly is crucial for creating tools that manage data close to its source. These devices play a vital role in factories where quick decisions and rapid data processing are essential. For instance, they enable faster responses by eliminating the need to transmit data to distant cloud servers.
Their significance in automation is rapidly increasing.
The market for industrial edge computing device assembly is projected to grow from USD 56.46 billion in 2025 to USD 106.25 billion by 2030, driven by the increasing adoption of automation in factories.
A survey conducted in 2023 revealed that 40.7% of businesses intended to implement industrial IoT technologies, highlighting the growing demand for edge devices.
These devices integrate seamlessly with industrial IoT systems, enhancing factory operations and boosting efficiency. They are a fundamental component of modern manufacturing. Ongoing advancements in industrial edge computing device assembly are shaping the future of automation.
Key Takeaways
Industrial edge devices handle data near where it is made. This helps factories make quick decisions and work better.
The demand for these devices is growing fast. It may reach $106.25 billion by 2030 because factories use more automation.
Edge computing helps predict problems with machines early. Factories can fix issues before they break and cost a lot.
These devices work with advanced tools like robots. They make robots work better and more reliably in automated systems.
Using edge computing saves money. It cuts down on sending data to the cloud and uses resources wisely.
Understanding Industrial Edge Computing Devices

What are industrial edge computing devices?
Industrial edge computing devices are tools that process data close to where it is created, like in factories or on production lines. They don’t need to send data to faraway cloud servers. This makes decisions faster and allows quick actions. These devices are tough and reliable, built to work in rough factory conditions.
Some important features of these devices are speed, quick response, and the ability to grow with more work. Speed shows how fast data is handled. Quick response means the system reacts fast to changes. Growth ability lets the device handle more tasks as factories expand. They also save energy, can be customized, and work with many factory systems.
Feature | What It Means |
|---|---|
Speed | Shows how fast data is processed and shared. |
Quick Response | Time it takes to react to changes, helping real-time tasks. |
Growth Ability | Handles more work and devices as factories grow. |
Energy Saving | Uses less power while doing more work, helping the environment. |
Workload Handling | Manages more tasks without slowing down. |
Custom Options | Can be changed to fit different factory needs. |
Compatibility | Works with many types of factory systems and tasks. |
Expandable Setup | Allows adding new tools and resources as needed. |
These features make edge computing devices very useful in modern factories.
How is edge computing different from cloud computing?
Edge computing and cloud computing are not the same. Edge computing works on data near where it is made, while cloud computing uses faraway servers. This difference affects speed, cost, and how well they work.
Edge computing is faster because it doesn’t send data far away. This is important for tasks that need quick answers, like checking product quality. It also uses less internet data, saving money. Cloud computing can be slower because data travels long distances and costs more to send.
Experts say spending on edge computing will reach $228 billion by 2024. This is because factories want faster systems and better automation. Edge computing is becoming more popular than cloud computing for these reasons.
Why are edge devices important in automation?
Edge computing devices are key to making factories run automatically. They process data quickly, predict problems, and connect with factory systems. This helps factories work better and avoid delays.
For example, an electric bike company saved $250,000 per hour by using edge devices. They had over 3,000 machines, and edge computing kept them running smoothly. These devices check machine health and find problems fast, helping factories save money.
Edge computing also fixes limits of IoT devices, which can’t handle big tasks alone. A study of 29 big companies showed edge computing helps share data better. This makes edge devices a must-have for modern factories.
The Role of Industrial Edge Computing in Automation
Real-time data processing and decision-making
Industrial edge devices process data instantly, helping quick and accurate decisions. They analyze data where it is made, avoiding delays from faraway servers. This is very important in industries like car-making or medicine production.
For example, car-making factories cut weld mistakes by 62% and rework costs by 28%. Medicine factories improved batch data accuracy to 99.998% and reduced quality checks by 43%. These changes save money and make work smoother.
Sector | Improvements |
|---|---|
Automotive Manufacturing | 62% fewer weld mistakes, 28% lower rework costs, 41% better first-time quality, $3.8 million saved yearly |
Pharmaceutical Production | 99.998% batch accuracy, 43% fewer quality checks, 67% faster rule submissions, Zero rule-breaking issues |
Food and Beverage | 22% better inventory tracking, 31% faster planning, 18% lower delivery costs, 27% less product waste |
Using real-time decisions keeps factories fast and ready for tough jobs.
Predictive maintenance and operational efficiency
Edge devices also help predict problems before machines break down. They watch equipment closely and find issues early, saving time and money. This reduces downtime and makes fixing machines more efficient.
With edge computing, repairs happen when needed, not on fixed schedules. Real-time data helps monitor machines and keeps them running safely. Maintenance takes less time and fewer workers, improving factory operations and reducing delays.
Supporting autonomous systems and robotics
Edge devices are key for robots and self-running systems. These tools process data quickly, reducing delays and improving robot performance. Fast data handling is crucial for tasks like safety checks and quality control.
Robots and self-running systems work better with edge computing. It makes them faster, more reliable, and efficient. Whether using robots in factories or self-driving vehicles in warehouses, edge devices ensure smooth operations.
Adding edge computing to automation boosts efficiency and innovation. These devices help process data fast, predict repairs, and support advanced technologies like robots.
Use Cases of Industrial Edge Computing in Manufacturing
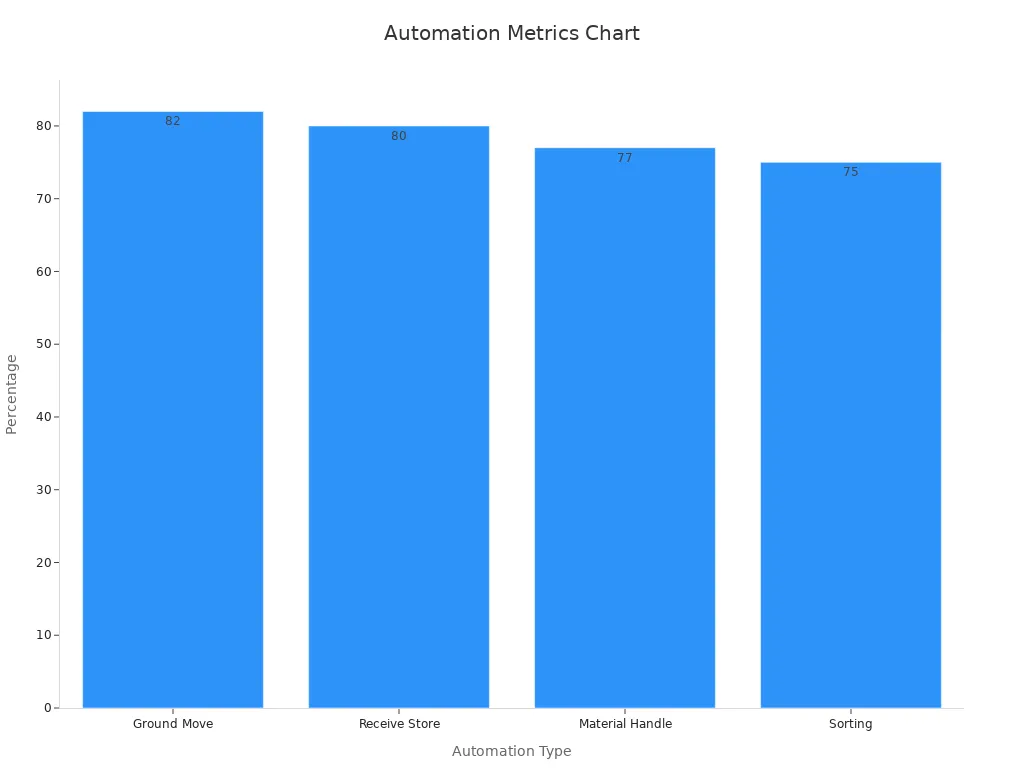
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and their reliance on edge computing
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) depend on edge computing to work well. These vehicles handle tasks like moving materials, sorting items, and ground transport. Edge computing helps AGVs process data instantly. This allows them to move, avoid obstacles, and plan routes quickly. It ensures smooth operations in busy factory environments.
AGVs using edge computing have made factories more efficient. For example, ground transport tasks now make up 82% of automated work. Material handling and sorting tasks reach 77% and 75%, respectively. These improvements lower labor costs and increase productivity. AGVs are becoming essential in modern factories. The AGV market is expected to grow to $3.3 billion by 2028.
Integration with industrial IoT (IIoT) systems
Edge computing devices are key to working with IIoT systems. They process data nearby, making decisions faster and needing less cloud use. This improves equipment monitoring, energy use, and maintenance predictions. These changes make manufacturing more efficient.
For example, smart defect inspection using AI has shown great results. It boosted productivity by 50% and improved defect detection by 90%. Combining edge computing with IIoT systems saves money and improves quality. It also makes factory operations run more smoothly.
Quality control and defect detection in production lines
Edge computing devices are changing how factories check quality and find defects. These devices analyze data right on the production line. This helps predict problems early and find defects faster. Unlike cloud systems, edge computing uses less internet and works better in real time.
A study on brake disc production showed how edge computing improves quality checks. A new control method predicted product quality better than older techniques. It solved issues like uneven data, giving more accurate results. Using edge computing can make production lines faster and reduce waste.
Benefits of Industrial Edge Computing in Automation
Saving money by using resources wisely
Industrial edge devices save money by handling data nearby. This means less data is sent to cloud servers, which costs more. Keeping temporary or small data at the edge saves internet use and storage fees. Companies like Enconnex and Exor show edge computing cuts costs by reducing cloud data transfers.
Source | Key Findings |
|---|---|
Enconnex | Edge computing saves bandwidth and lowers cloud storage costs. |
Exor | Storing temporary data locally reduces costs for big datasets. |
ITI College | Local data handling cuts delays and saves bandwidth. |
These savings make edge computing a smart choice for factory automation.
Working faster and avoiding delays
Edge computing makes factories work better by processing data instantly. This helps make quick decisions and avoid slowdowns. For example, edge devices watch machines and spot problems early. This stops breakdowns and saves repair time.
The need for fast data handling has improved edge computing. It sends only important data to the cloud, saving network space. This boosts productivity by helping factories run smoothly and make faster choices.
Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
Network Efficiency | Local data handling reduces internet use and improves speed. |
Real-time Data Processing | Quick decisions lower delays and increase productivity. |
Predictive Maintenance | Early problem detection prevents breakdowns and saves money. |
Using edge computing keeps factories efficient and productive.
Keeping data safe and private
Edge devices protect data by processing it locally. This lowers the chance of data being stolen during cloud transfers. Some governments now require data to stay within the country, making edge computing even more useful.
Studies show edge computing includes strong security tools like encryption. These tools keep data safe and follow privacy rules.
Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
Data Sovereignty Regulations | Local data processing improves security and meets government rules. |
Enhanced Security Solutions | Encryption and secure transfers protect sensitive information. |
Edge computing keeps your data safe and follows laws, making it a trusted option for automation.
The Future of Industrial Edge Computing in Manufacturing
Trends in industrial edge computing device assembly
Industrial edge computing devices are changing how factories work. These devices are being added to smart systems to improve work and lower risks. By handling data near its source, edge computing makes operations faster and more reliable. Robots and smart tools use this real-time data to work better.
New technologies like IoT and 5G are helping this change. They allow quick communication, which is needed for real-time tasks. Because of this, edge computing is becoming very important in modern factories. Experts predict the market will grow to $461.79 billion by 2032, with a yearly growth rate of 48.6%.
Year | Market Size (USD) | CAGR (%) |
|---|---|---|
2023 | 13.04 Billion | N/A |
2032 | 461.79 Billion | 48.6% |
Transforming traditional manufacturing processes
Edge computing is changing old factory methods by helping quick decisions and improving efficiency. Factories can now react fast to changes, avoiding delays and working better. Edge devices handle data locally, making them faster and safer since data doesn’t travel far.
This change also saves money. Edge computing sends only important data to the cloud, cutting costs and making work smoother. Factories using edge devices report faster data analysis and better equipment management, making their processes more reliable.
Quick decisions make factories respond faster.
Local data handling improves safety and speed.
Sending less data saves money and simplifies work.
Challenges and opportunities for adoption
Using edge computing in factories has both problems and benefits. It helps with faster automation, better data handling, and stronger security. But setting up edge systems with older tools needs expert knowledge. Small businesses may struggle with the high costs of edge devices and software.
Keeping data safe is another big issue. Local data handling needs strong security to stop hacking. These problems also bring chances to create new solutions. Fixing these issues can unlock edge computing’s full power, making factories smarter and more efficient.
Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
Hard Setup | Connecting edge systems to old tools needs expert skills. |
Data Safety Risks | Local data handling needs strong security to stop hacking. |
High Costs | Buying edge tools and software can be too expensive for small businesses. |
Industrial edge computing devices are important for today’s automation. They work fast, boost efficiency, and help advanced tools like robots. These devices change factories by making quick decisions and predicting repairs. Handling data nearby makes them faster and keeps information safer.
Using edge computing can open new possibilities for factories. These tools give useful details about how factories perform. They help improve processes and save money. Adopting this technology can help your business stay ahead in a tough market.
FAQ
What do industrial edge computing devices do?
Industrial edge devices handle data close to where it’s made. They help factories make quick decisions, improve automation, and work more efficiently. These devices are useful for predicting problems and helping robots work better.
How do edge devices help smart factories?
Edge devices make smart factories faster and more productive. They process data nearby, cutting delays and speeding up decisions. This improves factory work, saves money, and boosts efficiency in automated systems.
Can edge devices work with older factory tools?
Yes, edge devices can connect with older factory tools. They upgrade systems without needing new equipment. These devices improve data use and automation while still working with older setups.
Are edge devices safe to use?
Edge devices keep data safe by handling it locally. This lowers risks from sending data to the cloud. They use encryption and other tools to protect private information and follow safety rules.
Which industries use edge devices the most?
Industries like car-making, medicine, and food production use edge devices often. These tools help factories check quality, avoid delays, and work better in these fields.
See Also
Exploring Industrial IoT Devices and Hardware Solutions Today
The Importance of PCBA in Automation for Industries
Leading IIoT Hardware Options for Industries in 2025
Enhancing Industrial Automation Efficiency Through PCBA Technology
Increasing Manufacturing Productivity with IIoT Device Solutions





